hysteresis is shown in Figure 2-11.
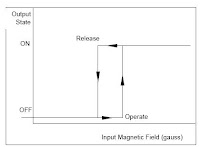
Figure 2-11 Transfer function hysteresis Digital output sensor
The principal input/output characteristics are the operate point,
release point and the difference between the two or differential.
As the magnetic field is increased, no change in the sensor output
will occur until the operate point is reached. Once the
operate point is reached, the sensor will change state. Further
increases in magnetic input beyond the operate point will have
no effect. If magnetic field is decreased to below the operate
point, the output will remain the same until the release point
is reached. At this point, the sensor’s output will return to
its original state (OFF). The purpose of the differential between
the operate and release point (hysteresis) is to
eliminate false triggering which can be caused by minor
variations in input.
The principal input/output characteristics are the operate point,
release point and the difference between the two or differential.
As the magnetic field is increased, no change in the sensor output
will occur until the operate point is reached. Once the
operate point is reached, the sensor will change state. Further
increases in magnetic input beyond the operate point will have
no effect. If magnetic field is decreased to below the operate
point, the output will remain the same until the release point
is reached. At this point, the sensor’s output will return to
its original state (OFF). The purpose of the differential between
the operate and release point (hysteresis) is to
eliminate false triggering which can be caused by minor
variations in input.
As with analog output Hall effect sensors, an output transistor
is added to increase application flexibility. This
output transistor is typically NPN (current sinking). See
Figure 2-12. The features and benefits are examined in detail
in Chapter 4.

Figure 2-12 NPN (Current sinking) . . . Digital output sensor
The fundamental characteristics relating to digital output
sensors have been presented. The specifications and the
effect these specifications have on product selection follows.
Source ( pdf )
Honeywel
http://content.honeywell.com/sensing/prodinfo/solidstate/technical/hallbook.pdf
The fundamental characteristics relating to digital output
sensors have been presented. The specifications and the
effect these specifications have on product selection follows.
Source ( pdf )
Honeywel
http://content.honeywell.com/sensing/prodinfo/solidstate/technical/hallbook.pdf





